Clamps are holding tools that grip, press, or secure materials tightly during work like cutting, joining, or welding. They help keep things in place so users can work safely and accurately. People use them in woodshops, metal shops, plumbing, and even in home repairs. In this post, you will learn about different clamp names and types. Each clamp has a different design and purpose. Learning these types of clamps with their pictures helps when talking about tools or doing any kind of hands-on work.
In This Page
Common Types of General-Purpose Clamps
These are used in everyday clamping jobs and fit many different tools and materials.
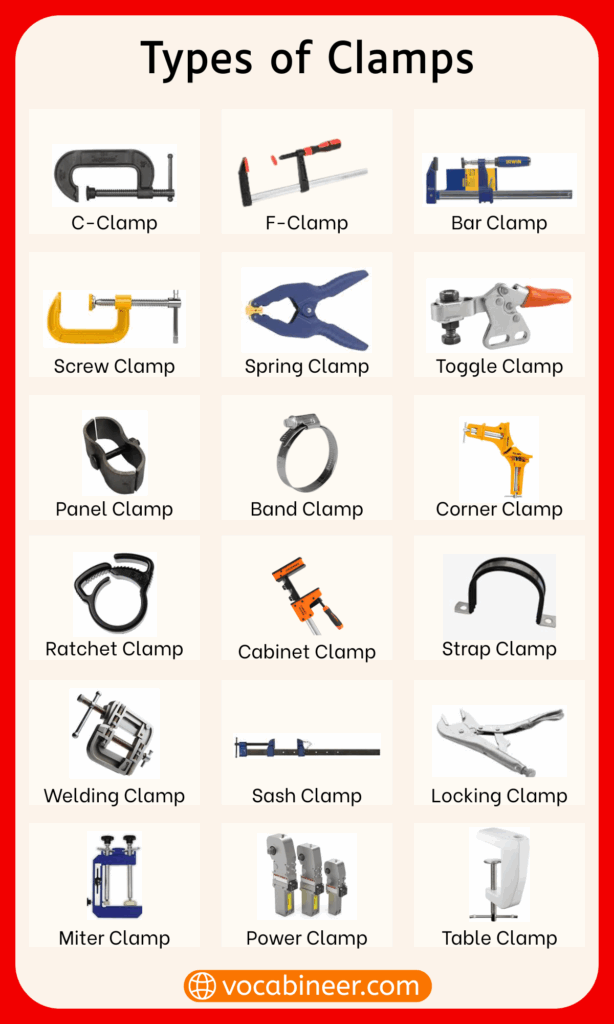
C Clamp (G Clamp): Has a C-shaped frame and screw, great for holding metal or wood firmly.
F Clamp (Sliding Arm Clamp): Resembles an F shape with an adjustable bar and fixed arm.
Bar Clamp (Speed Clamp): Long and sturdy, useful for wide or large surfaces.
Spring Clamp (Hand Clamp): Uses spring tension to grip quickly; often used for crafts or light pressure.
Hand Screw Clamp (Wood Hand Clamp): Uses two threaded screws for even and adjustable pressure on wood pieces.
List of Clamps Used in Woodworking Projects
Woodworkers rely on clamps to keep joints steady and parts aligned during gluing or cutting.
Pipe Clamp (Barrel Clamp): Uses a pipe as a bar to hold long or wide boards tightly.
Corner Clamp (Right-Angle Clamp): Keeps wood in a perfect 90-degree angle during frames or box joints.
Toggle Clamp (Holding Clamp): Locks and releases fast, often mounted on jigs or work tables.
Quick-Grip Clamp (One-Handed Clamp): Easy to use with one hand for quick tasks.
Band Clamp (Strap Clamp): Uses a strong fabric strap to secure round or irregular shapes like chair frames.
Types of Clamps for Metalworking and Welding
These clamps are made for high heat and strong hold needed in metal projects.
Locking Clamp (Welding Vise Grip): Holds metal parts tightly, often with padded or wide jaws.
Ground Clamp (Weld Ground Connector): Connects the welding machine to the metal being welded.
Magnetic Clamp (Mag Clamp): Uses magnets to hold flat or round steel parts during welding.
G Clamp (Cast Iron Clamp): Similar to C-clamps, but heavier and used in heavy-duty tasks.
Kant-Twist Clamp (Pivot Clamp): Combines pressure with twist action without shifting the workpiece.
Pipe Holding and Tubing Support Clamps Names
Used to secure pipes and tubes in plumbing, HVAC, or construction jobs.
Pipe Hanger Clamp: Suspends horizontal pipes from ceilings or beams.
Tube Clamp (Tubing Bracket): Used for lightweight tubing in labs, machines, or industries.
Split Ring Clamp (Two-Piece Clamp): Wraps around a pipe with two halves bolted together.
Riser Clamp (Vertical Pipe Clamp): Supports vertical pipes in tall buildings or installations.
Saddle Clamp (U-Bolt Clamp): Often used in outdoor piping, wraps around the pipe and fastens to a surface.
Beam Clamp: Attaches piping to structural steel without welding or drilling.
Cushioned Clamp: Features rubber padding to prevent damage to sensitive tubes or pipes.
Strut Clamp: Holds pipes to framing channels, often used in building systems and utilities.
Names of Clamps Used for Panels, Sheets, and Edges
These help hold large flat items or help align edges.
Panel Clamp (Flat Work Clamp): Aligns and secures wide boards or panels together during glue-ups.
Edge Clamp (Side Pressure Clamp): Applies pressure from the side to keep edges flush.
Face Clamp (Flush Surface Clamp): Holds surfaces even during pocket-hole joinery.
Parallel Jaw Clamp (Even Pressure Clamp): Keeps jaws parallel for even pressure across the whole surface.
Specialty and Industry-Specific Clamps
These are used in specific industries or special jobs where general clamps may not work.
Picture Frame Clamp: Keeps all corners of a picture frame tight and aligned.
Mitre Clamp (Angle Joint Clamp): Holds angled joints together during gluing or fastening.
Hose Clamp (Pipe Fastener): Tightens around flexible hoses to seal connections.
Toggle Latch Clamp (Latch Action Clamp): Often used on boxes, lids, or doors that need to stay shut firmly.
T-Bar Clamp (Heavy-Duty Bar Clamp): Larger version of a bar clamp with added strength and reach.
Glass Clamp: Used in displays and construction to secure glass panels safely.
Spindle Clamp: Often found in CNC tools or lathes for workpiece stabilization.
Battery Clamp: Used to connect battery terminals securely, often in cars or electronics.
Clamps Classified by Mechanism or Motion
Grouped by how they apply force or how they’re operated.
Ratchet Clamp (Step-Lock Clamp): Tightens step by step with a ratchet mechanism.
Lever Clamp (Quick Lever Clamp): Closes with a lever, often in one strong motion.
Cam Clamp (Cam-Action Clamp): Uses a rotating cam to quickly apply pressure.
Screw Clamp (Threaded Rod Clamp): Uses a threaded screw to move the jaw slowly with strong grip.
Pneumatic Clamp (Air Clamp): Uses air pressure to hold parts, often in factories or machines.
FAQs about Types of Clamps
A C clamp and a G clamp are the same in function. The name changes depending on region or shape preference. Both are shaped like the letter C or G and are used for strong, stable pressure on wood or metal.
The pipe clamp, corner clamp, and quick-grip clamp are widely used in woodworking. These clamps help hold wooden boards together while cutting, gluing, or assembling projects.
No, different clamps serve different jobs. For example, bar clamps are better for wide surfaces, while spring clamps are great for light holding. Choosing the right clamp depends on the size, material, and purpose.
Locking clamps, magnetic clamps, and ground clamps are commonly used in welding. They hold metal parts steady and help complete welds safely and accurately.
Check what material you’re working with and what kind of hold you need. For pipes, use saddle clamps or riser clamps. For woodworking, use F clamps or band clamps. Each clamp has a purpose that fits a specific task.
Read More




