Homonyms and homophones often cause confusion because both terms involve words that are alike in some way. A homonym is a word that shares spelling or pronunciation with another but carries a different meaning. A homophone is a word that sounds the same as another but has a different spelling and meaning. In this article, we’ll look at the definitions, examples, and differences between homonyms and homophones. We’ll also compare them with homographs to make the distinctions clearer.
In This Page
What Are Homonyms?
Homonyms are words that either share the same spelling or the same sound but have different meanings. The context of the sentence usually tells us which meaning is intended.
Examples of Homonyms:
- Bat: a flying animal → Bat: an object used in sports
- Bank: the side of a river → Bank: a place to keep money
- Fair: just or honest → Fair: a place with rides and games
- Spring: a season → Spring: a coil of metal
- Well: healthy → Well: a deep hole for water
Homonyms can be both homophones and homographs, which is why they are sometimes confusing.
What Are Homophones?
Homophones are words that sound the same but are spelled differently and carry different meanings. They are common in English and often create spelling mistakes for learners.
Examples of Homophones:
- Pair: a set of two → Pear: a fruit
- Sea: large body of water → See: to look at
- Flower: part of a plant → Flour: powder used in baking
- Right: correct → Write: to form letters or words
- Two: number 2 → Too: also → To: a preposition

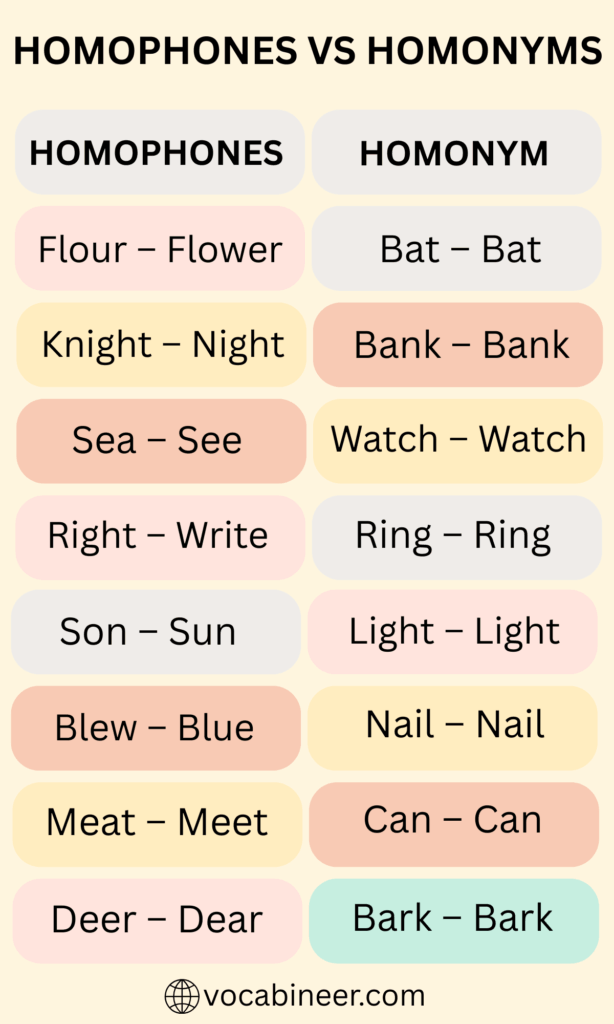
Homonym vs Homophone: Quick Comparison
Here’s a simple chart to highlight the main differences:
| Feature | Homonym | Homophone |
|---|---|---|
| Spelling | Same or different | Different |
| Sound | Same or different | Always the same |
| Meaning | Always different | Always different |
| Examples | Bat (animal/sports), Bank (river/money) | Pair/Pear, Right/Write, Sea/See |
Homonym Examples in English
Let’s look at more common homonyms used in daily English:
- Park: a green area → Park: to stop a car
- Match: a contest → Match: a stick that lights fire
- Kind: type → Kind: gentle and caring
- Rock: a stone → Rock: a style of music
- Letter: a character in writing → Letter: a written message
Homophone Examples in English
Homophones are especially important for spelling practice. Here are more examples:
- Bear: an animal → Bare: uncovered
- Hour: 60 minutes → Our: belonging to us
- Plain: simple → Plane: an aircraft
- Eye: organ for seeing → I: pronoun
- Break: to separate → Brake: device for slowing a car
Homonym vs Homophone in Sentences
Homonyms and homophones can look similar as terms, but their use in sentences makes the difference easy to understand. Homonyms share the same spelling or sound but have different meanings. Homophones always sound alike but are spelled differently. Below are examples in sentences that highlight the difference.
Homonym Sentences
- Bat: He swung the bat at the ball. → A bat flew across the night sky.
- Well: She is feeling well today. → The farmer pulled water from the well.
- Park: We had lunch at the city park. → Please park your car near the entrance.
- Match: The match ended in a draw. → Light the candle with a match.
- Spring: Flowers bloom in the spring. → The mattress has a broken spring.
Homophone Sentences
- Sea / See: The sea looks calm today. → I can see the island from here.
- Pair / Pear: She bought a pair of shoes. → He ate a juicy pear for lunch.
- Flower / Flour: A red flower grew in the garden. → Mix the flour with sugar and eggs.
- Right / Write: She gave the right answer. → Please write your name at the top.
- Two / Too / To: I have two pencils. → May I come along too? → Give this book to your sister.
Comparing Homonym and Homophone Sentences
- Homonym: The word well means both “healthy” and “a water source.”
- Homophone: The words flower and flour sound the same but have different spellings and uses.
Why They’re Often Confused
Both homonyms and homophones involve similarity either in sound or spelling. Since some homonyms also function as homophones, learners often mix them up. For example, “stalk” can mean the stem of a plant or the act of following someone. It sounds the same in both uses, making it both a homonym and homophone.
Homonym vs Homophone vs Homograph
To complete the picture, let’s add homographs to the mix:
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Homonym | Same spelling or sound, different meaning | Bat (animal/sports) |
| Homophone | Same sound, different spelling and meaning | Pair/Pear |
| Homograph | Same spelling, different meaning (may sound same) | Lead (metal) / Lead (to guide) |
Conclusion
Homonyms and homophones are closely related but not the same. A homonym can share spelling or sound but always carries a different meaning, while a homophone always sounds the same but has a different spelling and meaning. Understanding the difference helps learners avoid confusion in writing and reading.
Read More