Root words form the building blocks of thousands of English words. By learning roots, you can figure out meanings even when words look new or difficult. Most root words come from Latin and Greek, and many still appear in everyday English.
In this article, you’ll learn the definition of root words, how they combine with prefixes and suffixes, a large A–Z list of common roots, and examples in sentences. You’ll also see tables and comparisons to make the concept simple.
In This Page
What Is a Root Word in English?
A root word is the main part of a word that shows its basic meaning. Other words are made by adding prefixes (before) or suffixes (after).
Easy Examples:
- Port = carry → transport (carry across), import (carry in)
- Bio = life → biology (study of life), biography (story of life)
- Dict = say → predict (say before), dictionary (book of words people say)
- Scrib = write → describe (write about), manuscript (writing by hand)
- Aud = hear → audience (people who hear), audio (sound you hear)
How Root Words Work?
A root word is the part of a word that carries the core meaning. Other parts like prefixes or suffixes are added to change or expand that meaning. For example, the root port means carry. When we add im-, it becomes import (carry in). Adding -able makes portable (able to be carried). This shows how roots stay the same, but the words around them change.
Building Words with Prefixes + Root
A prefix attaches to the beginning of a root word to change its meaning.
- pre + dict → predict (say before)
- trans + port → transport (carry across)
- re + act → react (act again)
Building Words with Root + Suffix
A suffix attaches to the end of a root word to change its function or form.
- act + ion → action (the process of doing)
- friend + ship → friendship (state of being friends)
- teach + er → teacher (a person who teaches)
Words with Both Prefixes and Suffixes
Some words use both a prefix and a suffix, growing from a single root into a longer form.
- un + teach + able → unteachable (not able to be taught)
- re + act + ion → reaction (the process of acting again)
- dis + connect + ed → disconnected (not connected anymore)
Prefix + Root + Suffix Examples in a Table
| Prefix | Root | Suffix | New Word | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| re- | act | -ion | reaction | the act of responding |
| un- | kind | -ness | unkindness | the state of being cruel |
| pre- | view | -ing | previewing | looking before |
| dis- | agree | -ment | disagreement | not in agreement |
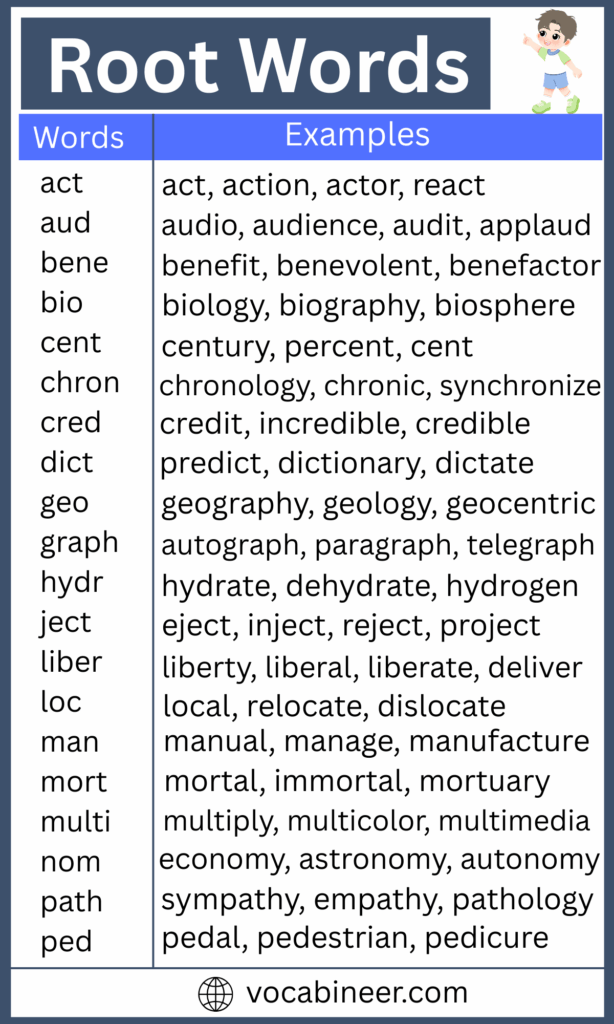
List of A to Z Root Words with Meanings
Root words are building blocks of English. Each has a simple meaning that helps form bigger words. Learning them makes it easier to understand new words. Below is a list of common root words with their meanings and examples.
- Act → do (action, react, actor)
- Aqua → water (aquarium, aquatic, aquaplane)
- Aud → hear (audio, audience, audition)
- Bell → war (rebellion, bellicose, antebellum)
- Bio → life (biology, biography, antibiotic)
- Chron → time (chronology, synchronize, chronic)
- Cred → believe (credit, incredible, credibility)
- Dict → say (dictionary, predict, contradict)
- Form → shape (transform, uniform, deform)
- Geo → earth (geography, geology, geothermal)
- Graph → write/draw (autograph, paragraph, graphic)
- Homo → same (homonym, homogenous, homosexual)
- Ject → throw (eject, inject, project)
- Loc → place (location, relocate, local)
- Meter → measure (thermometer, barometer, speedometer)
- Morph → form (metamorphosis, morphology, amorphous)
- Nav → ship (navigate, naval, navy)
- Oct → eight (octagon, octopus, octave)
- Path → feeling (sympathy, empathy, apathy)
- Phon → sound (telephone, microphone, phonics)
- Photo → light (photograph, photosynthesis, photocopy)
- Port → carry (transport, import, export)
- Quest/Quer → ask (question, inquire, request)
- Rupt → break (interrupt, erupt, rupture)
- Scrib/Script → write (describe, manuscript, inscription)
- Spec → see/look (inspect, spectator, spectacle)
- Struct → build (construct, structure, instruct)
- Tele → far (telephone, telescope, television)
- Therm → heat (thermal, thermostat, thermometer)
- Vid/Vis → see (video, visible, vision)
Root Word Examples in Sentences
- The audience clapped after the song. (Aud = hear)
- She read a biography of a famous leader. (Bio = life)
- We took a photo of the garden. (Photo = light)
- The workers will construct a bridge. (Struct = build)
- Please describe your best friend. (Scrib = write)
- The car’s speedometer showed 60 miles per hour. (Meter = measure)
- We learned about geography in class. (Geo = earth)
- He had to eject the old disk from the computer. (Ject = throw)
- That story is not credible at all. (Cred = believe)
- I used a telescope to see the moon. (Tele = far)
Comparison of Root Word vs Base Word
| Feature | Root Word | Base Word |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Carries the core idea | Can stand alone |
| Example | dict = to say | play, help, kind |
| Usage | Needs affixes | Works as a full word |
How to Learn Root Words Easily?
Start by noticing the repeating parts in long words. Group words by roots and practice with a chart. Use flashcards with the root on one side and meanings with examples on the other. Reading science and school texts also gives plenty of practice with roots.
FAQs About Root Words
A root word is the simplest form of a word that holds the main meaning. Other words are built from it using prefixes and suffixes.
A base word can stand alone (like happy), while a root word sometimes can’t (like bio). Roots are the foundation of many words.
Yes, the majority of English root words come from Latin and Greek. However, some also come from Old English and other languages.
Common examples include bio (life), port (carry), dict (say), and scrib/script (write). These appear in hundreds of English words.
Learning root words helps you guess the meaning of new words. It improves vocabulary, spelling, and reading comprehension.
Read More