The human body is made up of many parts that work together to support movement, thinking, breathing, eating, and other daily activities. Each body part has a specific role, whether it helps us see, hear, walk, hold objects, or keep vital organs functioning properly. Learning parts of body names allows readers to correctly identify different body areas and talk about them confidently in everyday conversations.
Understanding body part names is also useful for basic health awareness, early education, and following instructions at school or home. This article presents body parts in a clear, name-based, and well-structured way, covering external and internal parts, sections for adults and children, and commonly searched body part categories to make learning simple and organized.
In This Page
External Body Parts
External body parts are the visible parts of the human body. These parts help with movement, balance, communication, and interaction with the surroundings. Each external body part has a specific function that supports daily activities such as walking, eating, speaking, holding objects, and expressing emotions.
Head And Face Parts
The head and face contain organs responsible for thinking, senses, and facial expressions.
- Head: Protects the brain and supports facial structures
- Hair: Protects the scalp and helps regulate body temperature
- Scalp: Holds hair roots and protects the skull
- Forehead: Covers the front part of the skull above the eyes
- Face: Helps with expressions and communication
- Eyes: Used for seeing and visual awareness
- Eyebrows: Protect eyes from sweat and dust
- Eyelashes: Prevent dust and small particles from entering eyes
- Nose: Used for breathing and smelling
- Nostrils: Allow air to enter and exit the nose
- Cheeks: Help in chewing and forming facial expressions
- Mouth: Used for eating, speaking, and breathing
- Lips: Help in speech and holding food
- Teeth: Used for biting and chewing food
- Tongue: Helps taste food and supports speech
- Chin: Supports lower face structure
- Jaw: Holds teeth and allows mouth movement
- Ears: Used for hearing and balance
Upper Body Parts
Upper body parts support posture, protect organs, and allow arm movement.
- Neck: Connects the head to the body and supports head movement
- Shoulders: Allow arm movement and carry upper body weight
- Chest: Protects heart and lungs
- Upper back: Supports posture and shoulder movement
- Lower back: Supports the spine and body weight
- Spine: Keeps the body upright and protects the spinal cord
- Waist: Connects upper body to lower body
- Abdomen: Protects digestive organs
Lower Body Parts
Lower body parts help with standing, movement, and balance.
- Hips: Support body weight and connect legs to torso
- Thighs: Provide strength for walking and running
- Knees: Allow bending and straightening of legs
- Legs: Support body weight and movement
- Calves: Help in walking and standing on toes
- Ankles: Allow foot movement and balance
- Feet: Support standing, walking, and balance

Internal Body Parts
Internal body parts are located inside the human body and cannot be seen from the outside. These parts perform vital functions that keep the body alive and working properly. Internal organs help with breathing, digestion, circulation, thinking, and waste removal. Each internal body part has a specific role that supports overall health and daily functioning.
Major Organs
Major organs control essential body activities and life processes.
- Brain: Controls thinking, memory, movement, and body functions
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body
- Lungs: Help in breathing and oxygen exchange
- Liver: Processes nutrients and removes toxins from blood
- Kidneys: Filter waste and balance fluids in the body
- Stomach: Breaks down food using digestive juices
- Small intestine: Absorbs nutrients from digested food
- Large intestine: Absorbs water and forms waste
Digestive System Parts
These parts work together to digest food and absorb nutrients.
- Mouth: Begins digestion by chewing food
- Esophagus: Carries food from mouth to stomach
- Stomach: Mixes food with acids to break it down
- Small intestine: Absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream
- Large intestine: Absorbs water and stores waste
- Liver: Produces bile to help digest fats
- Pancreas: Releases enzymes for digestion
Respiratory System Parts
Respiratory parts allow breathing and oxygen supply.
- Nose: Filters and warms inhaled air
- Nasal cavity: Cleans and moistens air
- Trachea: Carries air to the lungs
- Bronchi: Direct air into each lung
- Lungs: Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
- Diaphragm: Helps control breathing movement
Circulatory System Parts
These parts move blood and oxygen around the body.
- Heart: Pumps blood through blood vessels
- Arteries: Carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart
- Veins: Return blood to the heart
- Capillaries: Allow oxygen and nutrients to reach tissues
- Blood vessels: Form the network for blood circulation
Parts Of The Head
The head is one of the most important parts of the human body. It contains the brain, which controls thinking and movement, along with sensory organs that help with seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, and feeling. The head also supports facial expressions, speech, and eating. Below are the main parts of the head, grouped clearly with their basic functions.
Facial Parts
Facial parts help with expressions, communication, and basic daily actions.
- Forehead: Covers the front part of the skull and supports facial expressions
- Eyes: Used for seeing and visual awareness
- Eyebrows: Protect the eyes from sweat and dust
- Eyelashes: Prevent small particles from entering the eyes
- Nose: Used for breathing and smelling
- Nostrils: Allow air to pass in and out of the nose
- Cheeks: Help in chewing and forming expressions
- Mouth: Used for eating, speaking, and breathing
- Lips: Help in speech and holding food
- Teeth: Used for biting and chewing
- Tongue: Helps in tasting and speaking
- Chin: Supports the lower face structure
- Jaw: Holds teeth and allows mouth movement
Sensory Organs
Sensory organs in the head receive information from the surroundings.
- Eyes: Detect light, color, and movement
- Ears: Used for hearing and balance
- Nose: Detects smells
- Tongue: Identifies taste
- Skin: Feels touch, temperature, and pain
Parts Of The Face
The face is the front part of the head and plays an important role in expressions, communication, breathing, and eating. Facial parts help show emotions, support speech, and allow basic daily actions such as seeing, smelling, and tasting. Each part of the face has a specific function that works together with other body systems.
Eyes And Eye Area Parts
The eye area supports vision and protects the eyes from dust and injury.
- Eyes: Used for seeing and visual understanding
- Eyelids: Protect the eyes and spread moisture
- Eyelashes: Block dust and small particles from entering the eyes
- Eyebrows: Prevent sweat from reaching the eyes
- Tear ducts: Produce tears to keep eyes clean and moist
Nose And Mouth Parts
The nose and mouth help with breathing, eating, speaking, and smelling.
- Nose: Used for breathing and smelling
- Nostrils: Allow air to move in and out
- Mouth: Used for eating, speaking, and breathing
- Lips: Help in speech and holding food
- Teeth: Used for biting and chewing
- Tongue: Helps with taste and speech
Other Facial Parts
These parts support structure and expressions of the face.
- Cheeks: Help with chewing and facial expressions
- Chin: Supports the lower face
- Jaw: Allows movement for chewing and speaking
Parts Of The Hand
The hand is one of the most useful parts of the human body. It helps with holding, writing, lifting, touching, and performing daily tasks. The hand works together with the fingers, palm, and wrist to allow precise movement, grip, and control. Each part of the hand has a specific function that supports everyday activities.
Finger Names
Fingers allow grasping, pointing, and fine motor movements.
- Thumb: Helps in gripping and holding objects firmly
- Index finger: Used for pointing and precise actions
- Middle finger: Provides strength and balance to the hand
- Ring finger: Supports grip and coordination
- Little finger: Helps in balance and fine control
Palm And Wrist Parts
These parts connect the hand to the arm and support movement.
- Palm: Holds objects and supports grip
- Wrist: Allows hand movement and connects the hand to the arm
- Knuckles: Help fingers bend and move
Other Hand Parts
Additional hand parts support protection and touch.
- Nails: Protect fingertips and improve grip
- Fingertips: Provide touch sensitivity and fine control
Parts Of The Leg
The leg is an important part of the body that supports standing, walking, running, and balance. It carries body weight and allows movement from one place to another. The leg works together with muscles, joints, and bones to provide strength, flexibility, and stability during daily activities.
Upper Leg Parts
Upper leg parts help support body weight and generate movement.
- Hip: Connects the leg to the body and supports body weight
- Thigh: The strongest part of the leg, used for walking, running, and jumping
Lower Leg Parts
Lower leg parts help with movement, balance, and bending of the leg.
- Knee: Allows the leg to bend and straighten
- Shin: The front part of the lower leg that supports movement
- Calf: Helps in walking, running, and standing on toes
- Ankle: Connects the leg to the foot and allows foot movement
Other Leg Parts
These parts support stability and daily movement.
- Leg muscles: Provide strength and control movement
- Leg bones: Support body weight and structure
Parts Of The Foot
The foot supports body weight and helps with standing, walking, running, and balance. It works together with the leg and ankle to absorb impact and maintain stability on different surfaces. Each part of the foot has a specific role that allows smooth movement and proper support during daily activities.
Toe Names
Toes help with balance, grip, and forward movement while walking.
- Big toe: Provides balance and helps push the body forward
- Second toe: Supports balance and walking movement
- Middle toe: Helps maintain stability while standing
- Fourth toe: Assists with balance and foot support
- Little toe: Helps stabilize the foot during movement
Sole And Heel Parts
These parts carry body weight and absorb pressure.
- Sole: Supports the bottom of the foot and absorbs impact
- Heel: Bears body weight and supports standing
- Arch: Helps distribute weight and maintain balance
Other Foot Parts
These parts protect the foot and support movement.
- Ankle: Allows foot movement and connects foot to leg
- Toenails: Protect the toes from injury
- Foot muscles: Help control foot movement and balance
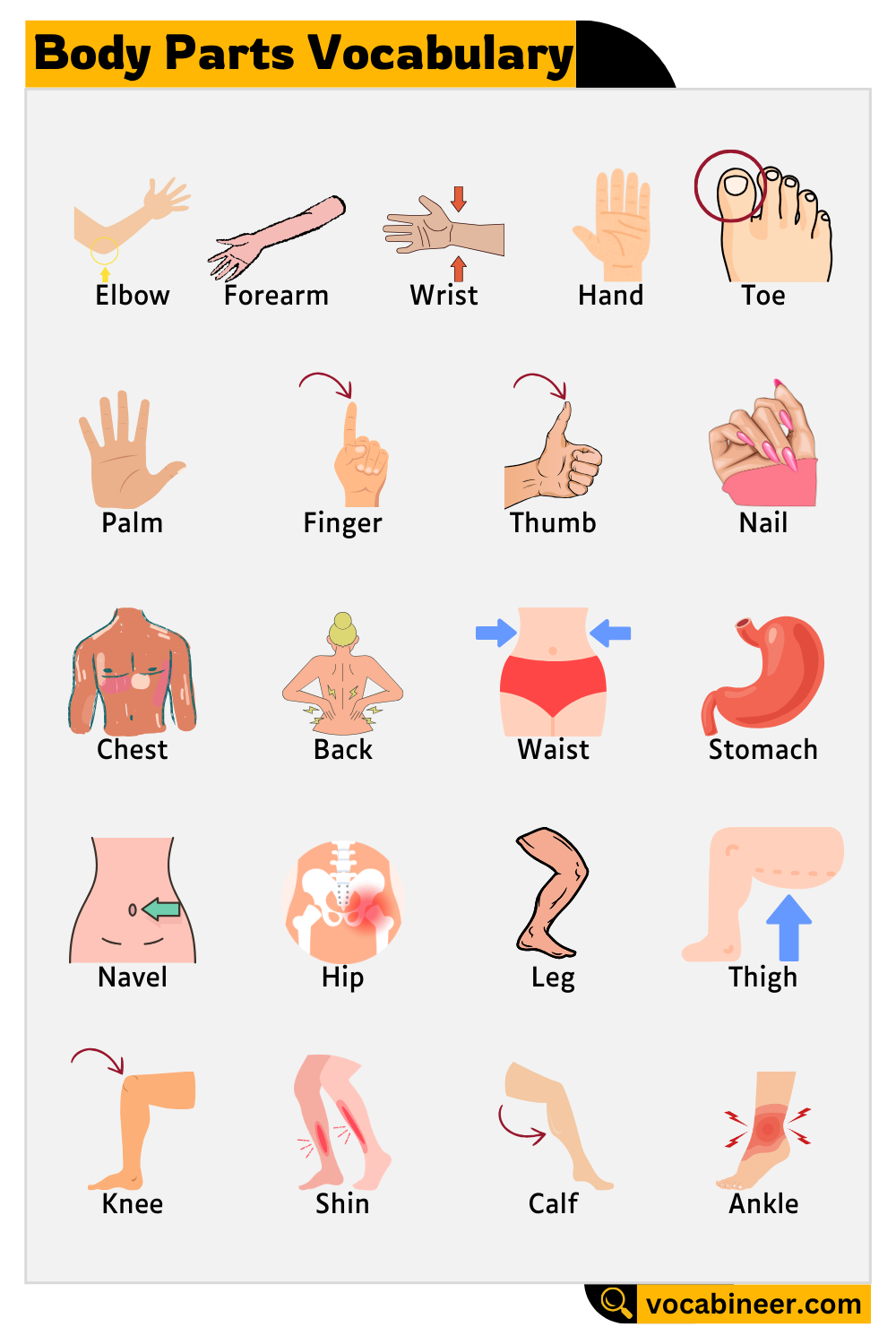
Body Parts By Function
Body parts can also be grouped based on what they do. This way of learning helps readers understand how different parts work together to perform specific tasks. Grouping body parts by function makes it easier to see how movement, breathing, digestion, and other daily activities happen smoothly.
Movement And Support Parts
These body parts help the body move, stay upright, and maintain balance.
- Bones: Form the framework of the body and support its shape
- Muscles: Help move body parts and control actions
- Joints: Allow bones to move and bend
- Arms: Used for lifting, holding, and carrying
- Hands: Help with gripping, writing, and fine tasks
- Legs: Support body weight and enable walking and running
- Feet: Maintain balance and support movement
Breathing And Circulation Parts
These parts help the body breathe and transport oxygen and blood.
- Lungs: Take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body
- Blood vessels: Carry blood to all body parts
- Arteries: Move oxygen-rich blood away from the heart
- Veins: Return blood to the heart
- Capillaries: Allow oxygen and nutrients to reach cells
Digestion And Absorption Parts
These body parts help process food and absorb nutrients.
- Mouth: Starts digestion by chewing food
- Teeth: Break food into smaller pieces
- Tongue: Helps with swallowing and tasting
- Stomach: Breaks down food using acids
- Small intestine: Absorbs nutrients into the body
- Large intestine: Absorbs water and forms waste
- Liver: Helps digest fats and process nutrients
Female Parts Of Body
This section lists commonly referenced external female body parts in a clear and educational way.
External Female Body Parts
- Head
- Hair
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Arms
- Hands
- Chest
- Waist
- Hips
- Legs
- Knees
- Ankles
- Feet
Upper Female Body Areas
- Shoulders
- Bust
- Upper back
- Arms
Lower Female Body Areas
- Hips
- Thighs
- Knees
- Legs
- Feet
Parts Of Body For Kids
These body parts are commonly taught to children for basic learning.
Basic Body Parts For Kids
- Head
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Mouth
- Hands
- Legs
- Feet
Body Parts Kids Learn Early
- Fingers
- Toes
- Teeth
- Hair
- Belly
- Back
Body Parts Used In Daily Activities
- Hands for holding
- Legs for walking
- Eyes for seeing
- Ears for hearing
Human Body Parts For Daily Use
Some body parts are used frequently in everyday activities.
Body Parts Used For Eating
- Mouth
- Teeth
- Tongue
Body Parts Used For Walking
- Legs
- Knees
- Feet
- Ankles
Body Parts Used For Seeing And Hearing
- Eyes
- Ears
Human Body Parts Name Chart
Below is a clear and easy-to-read human body parts name chart that lists common body parts along with their basic functions. This chart helps learners quickly identify body parts and understand what each part does in daily life.

| Body Part | Category | Basic Function |
|---|---|---|
| Head | External | Protects the brain and supports facial parts |
| Hair | External | Protects the scalp and helps regulate temperature |
| Eyes | External | Used for seeing |
| Ears | External | Used for hearing and balance |
| Nose | External | Helps with breathing and smelling |
| Mouth | External | Used for eating and speaking |
| Teeth | External | Bite and chew food |
| Tongue | External | Helps with taste and speech |
| Neck | External | Connects head to body and allows movement |
| Shoulders | External | Support arm movement |
| Arms | External | Used for lifting and carrying |
| Hands | External | Help with holding and writing |
| Fingers | External | Allow grip and fine movement |
| Chest | External | Protects heart and lungs |
| Back | External | Supports posture and movement |
| Waist | External | Connects upper and lower body |
| Hips | External | Support body weight |
| Thighs | External | Help in walking and running |
| Knees | External | Allow bending of legs |
| Legs | External | Support standing and movement |
| Ankles | External | Allow foot movement |
| Feet | External | Support balance and walking |
| Brain | Internal | Controls thinking and body functions |
| Heart | Internal | Pumps blood |
| Lungs | Internal | Help in breathing |
| Stomach | Internal | Digests food |
| Liver | Internal | Processes nutrients |
| Kidneys | Internal | Remove waste from blood |
| Small Intestine | Internal | Absorbs nutrients |
| Large Intestine | Internal | Absorbs water and forms waste |
FAQs about Human Parts of Body
The main parts of the human body include the head, neck, torso, arms, and legs. Each of these areas contains smaller parts that support movement, senses, and daily activities.
External body parts are the parts that can be seen from the outside. These include the face, hands, arms, legs, feet, eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.
Internal body parts are located inside the body and are not visible. Common internal parts include the brain, heart, lungs, stomach, liver, kidneys, and intestines.
Learning body part names helps people communicate clearly, understand basic health topics, and follow instructions in education, daily life, and healthcare settings.
Movement is supported by legs, arms, muscles, joints, and bones. These parts work together to allow walking, lifting, bending, and other actions.
Children usually learn names of basic body parts such as head, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, hands, legs, and feet first.
Eyes help with seeing, while ears are used for hearing. Both are important sensory organs used every day.
Read More



