Math symbols are special signs used to represent numbers, actions, relationships, and ideas in mathematics. Instead of long sentences, these symbols communicate meaning quickly and precisely. They are used in basic calculations, algebraic expressions, geometric figures, and advanced mathematical formulas.
Learning math symbols helps readers understand equations, follow problem-solving steps, and read mathematical text correctly. Because symbols are consistent across textbooks and classrooms, knowing them allows students to work confidently with numbers and formulas.
In This Page
What are math symbols?
Math symbols are visual representations of mathematical operations, values, or relationships. Each symbol has a fixed meaning that does not change based on context. For example, the plus sign always represents addition, and the equals sign always shows equality between two values.
Understanding what math symbols mean allows readers to read equations as complete ideas rather than isolated marks. When symbols are misunderstood, even simple problems can become confusing. Knowing symbol meanings helps learners translate written math into logical steps and accurate solutions.
Why Math Symbols Are Used?
Math symbols are used to make mathematical communication clear, short, and efficient. Writing full sentences for every calculation would make math slow and difficult to read. Symbols replace words so that ideas can be expressed in a compact form.
These symbols are especially important in textbooks, exams, and scientific writing, where space and clarity matter. They also allow people across different languages and countries to understand the same mathematical ideas, since most math symbols are recognized worldwide.
Commonly Used Math Symbols
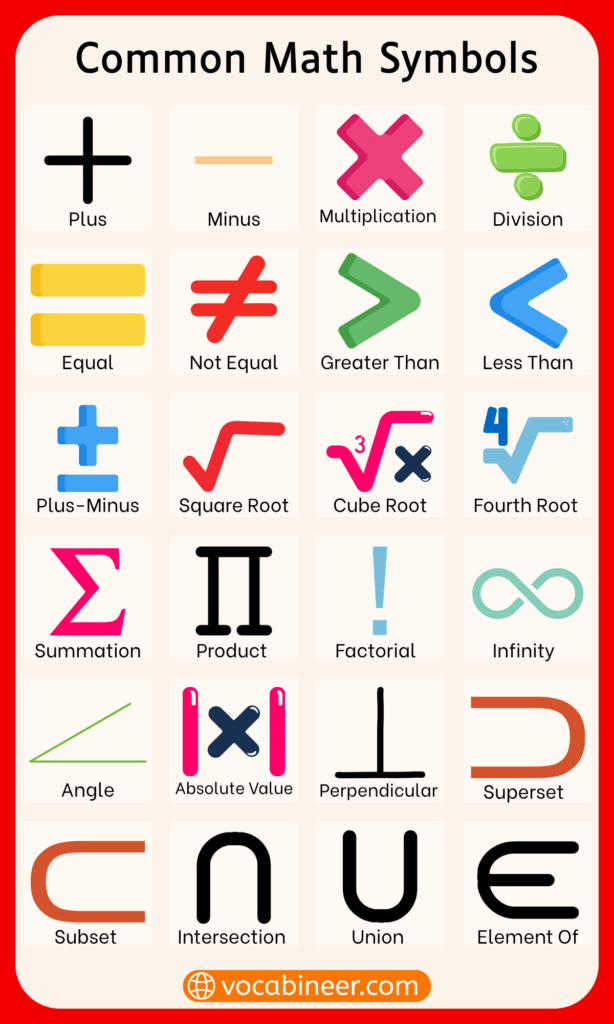
Common math symbols appear in almost every area of mathematics, from basic arithmetic to advanced topics. These symbols form the foundation of mathematical language.
- + Plus: Used to add numbers together and find a total
- − Minus: Used to subtract one number from another
- × Multiplication: Shows repeated addition of a number
- ÷ Division: Splits a number into equal parts
- = Equals: Shows that two values are the same
- ≠ Not equal: Shows that two values are different
- < Less than: Indicates a smaller value compared to another
- > Greater than: Indicates a larger value compared to another
- ≤ Less than or equal to: Shows a value is smaller or the same
- ≥ Greater than or equal to: Shows a value is larger or the same
- ± Plus minus: Indicates both addition and subtraction possibilities
- % Percent: Represents a part out of one hundred
- √ Square root: Finds a number that multiplies by itself to give a value
- ∞ Infinity: Represents an endless or unbounded quantity
Symbols Common in Algebra
Algebra symbols are used to represent unknown values, constants, and relationships between numbers. These symbols help turn word problems into equations that can be solved step by step. Algebra relies on symbols to show patterns, balance, and change in mathematical expressions.
- x Variable: Represents an unknown number that needs to be found
- y Variable: Another unknown value, often related to x
- a Constant: A fixed number that does not change
- b Constant: Another fixed value used in expressions
- = Equality: Shows both sides of an equation have the same value
- ≠ Inequality: Shows two expressions are not equal
- ^ Exponent: Indicates repeated multiplication
- √ Root: Finds the base value of a number
- ∑ Summation: Adds a series of values together
- → Mapping: Shows how one value relates to another
- ↔ Equivalence: Shows two expressions represent the same idea
- ∝ Proportional: Shows values increase or decrease together
Symbols Used in Geometry
Geometry symbols are used to describe shapes, lines, angles, and measurements. These symbols help explain how figures are formed and how they relate to one another in space. Geometry depends on symbols to show structure and position clearly.
- ∠ Angle: Measures the space between two lines
- ° Degree: Shows the size of an angle
- △ Triangle: A shape with three sides
- □ Square: A shape with four equal sides
- ▭ Rectangle: A shape with opposite sides equal
- ○ Circle: A round shape with all points equally distant from the center
- ⊥ Perpendicular: Shows lines meeting at a right angle
- ∥ Parallel: Shows lines that never meet
- π Pi: Used to calculate circle measurements
- r Radius: Distance from center to edge of a circle
- d Diameter: Distance across a circle through the center
Trigonometry Symbols You Should Know
Trigonometry symbols are used to study the relationships between angles and sides of triangles. These symbols are common in problems involving height, distance, and angles. They help connect geometry with algebra.
- sin Sine: Ratio of opposite side to hypotenuse
- cos Cosine: Ratio of adjacent side to hypotenuse
- tan Tangent: Ratio of opposite side to adjacent side
- csc Cosecant: Reciprocal of sine
- sec Secant: Reciprocal of cosine
- cot Cotangent: Reciprocal of tangent
- θ Theta: Represents an unknown angle
- π Pi: Used in radian measurements
- ° Degree: Unit for measuring angles
Symbols Used in Calculus
Calculus symbols describe change, motion, and accumulation. These symbols are used to study how values change over time or how areas and volumes are calculated. Calculus relies heavily on symbols to express complex ideas simply.
- ∫ Integral: Represents the area under a curve
- ∮ Contour integral: Integral taken around a closed path
- d Differential: Represents a very small change
- dx Derivative: Rate of change with respect to x
- ∂ Partial derivative: Change with respect to one variable
- lim Limit: Value that a function approaches
- ∞ Infinity: Represents unbounded growth
- ∑ Summation: Adds infinite or finite series
- ∇ Nabla: Used for gradients and vector calculus
Symbols That Compare Values
Comparison symbols are used to show how two numbers or expressions relate to each other. These symbols help readers understand whether values are equal, larger, smaller, or only close in size. They are common in arithmetic, algebra, and data analysis.
- = Equals: Shows two values have the same quantity
- ≠ Not equal: Shows two values are different
- < Less than: Indicates one value is smaller than another
- > Greater than: Indicates one value is larger than another
- ≤ Less than or equal to: Shows a value is smaller or the same
- ≥ Greater than or equal to: Shows a value is larger or the same
- ≈ Approximately equal: Shows values are close but not exact
- ≡ Identical: Shows exact equivalence in value or form
- ∝ Proportional: Shows values change together at a constant rate
Symbols Used in Set Theory
Set theory symbols are used to describe collections of numbers or objects and how those collections relate to one another. These symbols help organize values into groups and explain membership and relationships clearly.
- ∅ Empty set: A set with no elements
- ∈ Element of: Shows a value belongs to a set
- ∉ Not element of: Shows a value does not belong to a set
- ⊂ Subset: Shows one set is part of another
- ⊆ Subset or equal: Shows a set is contained within another
- ⊃ Superset: Shows a set contains another set
- ⊇ Superset or equal: Shows full containment
- ∪ Union: Combines elements from sets
- ∩ Intersection: Shows common elements
- | Such that: Describes a condition within a set
Logic Symbols Used in Math
Logic symbols are used to express reasoning, conditions, and conclusions in mathematics. These symbols help build arguments and prove statements step by step, especially in higher-level math.
- ∧ And: Both conditions must be true
- ∨ Or: At least one condition is true
- ¬ Not: Reverses a statement
- ⇒ Implies: One statement leads to another
- ⇔ If and only if: Two statements depend on each other
- ∀ For all: Applies to every element
- ∃ There exists: At least one element exists
- ∴ Therefore: Shows a conclusion
Measurement and Unit Symbols
Measurement symbols represent size, length, weight, time, and other quantities. These symbols are used in math, science, and daily calculations to express values accurately.
- m Meter: Basic unit of length
- cm Centimeter: One hundredth of a meter
- km Kilometer: One thousand meters
- kg Kilogram: Unit of mass
- g Gram: Smaller unit of mass
- s Second: Unit of time
- ms Millisecond: One thousandth of a second
- ° Degree: Unit for angles or temperature
- ′ Minute: Unit of time or angle
- ″ Second: Smaller unit of time or angle
Symbols Used in Number Systems
Number system symbols are used to classify numbers into different groups based on their properties. These symbols help explain what type of numbers are being used in an equation and how they behave. They are important for understanding higher math concepts and number relationships.
- ℕ Natural numbers: Counting numbers starting from 1
- ℤ Integers: Whole numbers including negatives and zero
- ℚ Rational numbers: Numbers written as fractions
- ℝ Real numbers: All numbers on the number line
- ℂ Complex numbers: Numbers with real and imaginary parts
- i Imaginary unit: Square root of −1
- 0 Zero: Represents no quantity
- 1 One: Multiplicative identity
- π Pi: Irrational constant used in circles
- e Euler’s number: Base of natural logarithms
Symbols Used in Probability and Statistics
Probability and statistics symbols are used to analyze data, measure uncertainty, and describe patterns. These symbols help summarize information and make predictions based on numerical evidence.
- P Probability: Likelihood of an event occurring
- μ Mean: Average value of a data set
- σ Standard deviation: Spread of data around the mean
- Σ Summation: Total of values
- n Sample size: Number of observations
- N Population size: Total number of elements
- x̄ Sample mean: Average of a sample
- p Probability value: Chance of success
- q Complement: Probability of failure
- | Given: Shows a condition
Greek Letters Used in Math
Greek letters are commonly used in mathematics to represent constants, angles, and variables. They help avoid confusion with regular letters and are widely accepted in math notation.
- α Alpha: Represents angles or constants
- β Beta: Used for coefficients
- γ Gamma: Represents angles or functions
- Δ Delta: Change in value
- ε Epsilon: Small quantity
- θ Theta: Angle measurement
- λ Lambda: Wavelength or eigenvalues
- μ Mu: Mean in statistics
- π Pi: Circle constant
- ρ Rho: Density or radius
- σ Sigma: Standard deviation
- ω Omega: Angular velocity
Advanced Symbols Used in Mathematics
Advanced math symbols appear in higher-level mathematics such as calculus, linear algebra, and logic. These symbols allow complex ideas to be expressed in a precise and compact form.
- ∇ Nabla: Gradient or vector operator
- ℵ Aleph: Size of infinite sets
- ⊕ Exclusive or: Logical operation
- ⊗ Tensor product: Combines vector spaces
- ≪ Much less than: Shows very small comparison
- ≫ Much greater than: Shows very large comparison
- ≃ Asymptotically equal: Values approach each other
- ⊥ Bottom: False in logic
- ⊤ Top: True in logic
Math Symbols That Often Cause Confusion
Some math symbols look similar or are used in different ways depending on the topic. This can confuse learners if the symbols are not clearly understood. Knowing the difference between these symbols helps avoid mistakes in calculations and interpretation.
- − Minus: Used for subtraction
- – Dash: Used to show ranges, not subtraction
- ≈ Approximately equal: Shows values are close
- ≃ Similar to: Shows values behave alike but are not equal
- ≅ Congruent: Shows shapes are identical in size and shape
- × Multiplication: Arithmetic operation
- · Dot: Alternative multiplication symbol
- | Absolute value: Distance from zero
- ‖ Parallel: Lines that never meet
- ⊥ Perpendicular: Lines meeting at right angle
Math Symbols Recognized Worldwide
Many math symbols are used the same way across different countries and languages. These symbols help people understand math universally, regardless of spoken language.
- + Plus: Addition
- − Minus: Subtraction
- × Multiply: Repeated addition
- ÷ Divide: Equal sharing
- = Equals: Same value
- < Less than: Smaller value
- > Greater than: Larger value
- ≤ Less than or equal to: Smaller or same value
- ≥ Greater than or equal to: Larger or same value
- % Percent: Part of one hundred
- √ Square root: Root value
- ∞ Infinity: Endless quantity
When to Use Math Symbols in Writing
Math symbols should be used in equations, formulas, calculations, and technical explanations where precision is important. They help shorten expressions and reduce confusion when working with numbers and relationships.
In regular writing, symbols should only be used when their meaning is widely understood. When clarity may suffer, words should be used instead of symbols.
Math Symbols Compared to Words
Math symbols and words are both used to communicate mathematical ideas, but they serve different purposes. Symbols focus on speed and precision, while words help explain meaning and reasoning in a clearer way. The table below compares math symbols and words to show when each is more appropriate to use.
| Aspect | Math Symbols | Words |
|---|---|---|
| Basic form | Visual signs and marks | Written language |
| Purpose | Show operations and relationships | Explain ideas and steps |
| Length | Very short | Can be short or long |
| Speed of understanding | Quick for trained readers | Slower but detailed |
| Usage area | Equations and formulas | Explanations and instructions |
| Precision | Very precise | Can vary by wording |
| Space required | Minimal | More space needed |
| Learning stage | Used after concepts are known | Used when learning concepts |
| Universality | Same across most countries | Changes by language |
| Best use case | Calculations and notation | Reasoning and description |
FAQs About Math Symbols
Math symbols are signs used to represent numbers, operations, relationships, and mathematical ideas in a short and clear form.
They help students read equations correctly, solve problems efficiently, and understand mathematical writing without confusion.
Most common math symbols are used worldwide, which makes mathematics a universal language across different cultures.
No. Symbols are used for calculations and expressions, while words are needed to explain reasoning and steps.
Math symbols appear in textbooks, exams, classrooms, scientific research, engineering, and everyday calculations.
Conclusion
Math symbols form the basic language of mathematics and allow ideas to be shared clearly and efficiently. Each symbol has a fixed meaning that helps represent numbers, operations, and relationships without long explanations. Learning these symbols makes it easier to read equations, follow problem-solving steps, and understand mathematical text.
By understanding both the meanings and proper uses of math symbols, readers can communicate mathematical ideas accurately and avoid common mistakes. Knowing when to use symbols and when to use words helps create clear and effective mathematical communication.
Read More




