Than vs Then often creates confusion because the words look similar and sound alike in fast speech. However, their meanings and grammar roles are completely different. One is used for comparison, while the other refers to time or sequence. Their spelling reflects conjunction versus adverb contrast.
Understanding Than vs Then helps you choose the correct word in structured writing, academic comparisons, and everyday communication. This article explains their meaning, grammar roles, usage patterns, sentence structure, and common mistakes so you can apply them accurately.
In This Page
Than vs Then: Quick Definition
Than is used for comparison.
Then refers to time, sequence, or result.
The key difference in Than vs Then is comparison versus time or order.
Than vs Then Difference in One Sentence
Than compares two things.
Then shows what happens next or at that time.
Why Than and Then Are Often Confused
Than and Then are often confused because they differ by only one letter. In addition, their pronunciation is very similar in casual speech. Therefore, writers sometimes use the wrong spelling when typing quickly.
However, their grammar roles are distinct. Than is a conjunction used in comparisons. Then is an adverb that refers to time or sequence. As a result, confusion usually happens when writers focus on sound instead of structure.
Word Origin and Etymology
The history of Than vs Then shows that both words developed from Old English roots connected to comparison and time. Than evolved as a comparison word used with adjectives and adverbs. Then developed as a time related word referring to sequence or a specific moment.
Over time, English maintained this separation. Therefore, Than signals comparison, while Then signals time or order.
What Does Than Mean?
Than is used to compare two things, people, or ideas.
Definition of Than
Than is a conjunction used to introduce the second element in a comparison.
It functions as a conjunction.
Than in Comparisons
Because Than is a conjunction, it connects two elements being compared.
Examples using Than:
- She is taller than her sister.
- This book is better than that one.
- He runs faster than I do.
- The test was easier than expected.
- I prefer tea than coffee.
- She is smarter than him.
- This car is more expensive than mine.
- Today is warmer than yesterday.
- He works harder than before.
- That movie was more interesting than the last one.
- She sings better than her friend.
- This route is shorter than the other.
- He arrived earlier than expected.
- The project was more complex than planned.
- I would rather stay home than go out.
- This problem is harder than it looks.
- She studies more than her classmates.
- The meal tasted better than usual.
- He finished later than me.
- This solution is simpler than the previous one.
Notice that Than always follows comparative forms like taller, more, better, or rather.
Common Uses and Collocations of Than
- Better than
- More than
- Less than
- Rather than
- Other than
- Faster than
- Bigger than
- Smaller than
- Higher than
- Lower than
- Older than
- Younger than
- More important than
- More difficult than
- More interesting than
What Does Then Mean?
Then refers to time, sequence, or what happens next. In the Than vs Then contrast, Then does not compare two things. Instead, it shows order, result, or a specific moment in time.
Unlike Than, which connects comparisons, Then connects events in sequence.
Definition of Then
Then is an adverb used to indicate time, order, or consequence.
It functions as an adverb.
Then as an Adverb
Because Then is an adverb, it modifies verbs or entire sentences to show time or sequence.
Examples using Then:
- We went home, and then we ate dinner.
- Finish your work, then relax.
- She studied hard, and then she passed.
- Back then, life was different.
- I will call you, and then we can decide.
- He apologized, and then he left.
- She paused, then continued speaking.
- First read the instructions, then begin.
- The lights went out, and then everything was dark.
- We met in 2020. Then, we moved abroad.
- Save the file, then close the program.
- He hesitated, then answered.
- Eat your vegetables, then have dessert.
- She smiled, then walked away.
- I did not understand it back then.
- Press the button, then wait.
- They argued, and then they apologized.
- He finished school and then got a job.
- She thought about it, then agreed.
- We will discuss it, then decide.
Notice something important. Then often appears after commas or at the beginning of a clause to show sequence.
Common Uses and Collocations of Then
- And then
- Back then
- Just then
- By then
- Since then
- Then again
- First then
- Now and then
- Until then
- If then
- Then suddenly
- Then later
- Then finally
- Then next
- Then afterwards
Each phrase relates to time, order, or result rather than comparison.
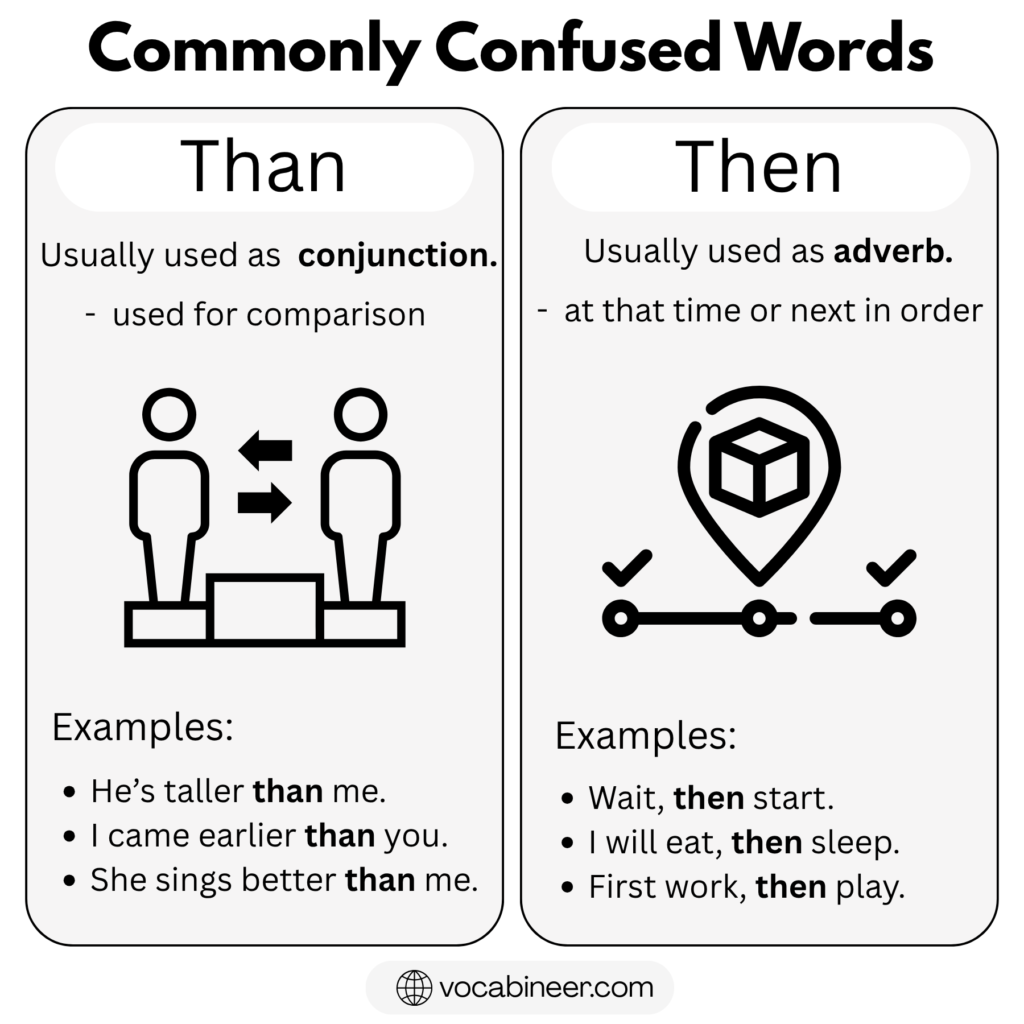
Than vs Then: Key Difference Explained
The main difference in Than vs Then depends on grammar role and meaning. Than is used only for comparison. Then refers to time, order, or result.
If the sentence compares two things, use Than.
If the sentence shows what happens next or refers to a time, use Then.
Here is the difference in one sentence:
Than compares.
Then shows sequence or time.
Than vs Then: Difference in One Look
| Feature | Than | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Part of Speech | Conjunction | Adverb |
| Meaning | Used for comparison | Refers to time or order |
| Context | Comparative sentences | Sequence or time references |
| Replace With | Compared with | Next, at that time |
| Common Structure | Better than | And then |
Notice something important. Than appears after comparative words like better, more, or less. Then usually appears when events follow each other.
Than vs Then: Side by Side Sentence Contrast
- She is taller than her sister.
- She finished school, and then she got a job.
- This problem is harder than the last one.
- Finish your homework, then go outside.
- He runs faster than me.
- He called me, and then he left.
In each pair, Than introduces comparison. Then shows order or sequence.
Than vs Then: Sentence Structure Comparison
Understanding structure makes the difference easier.
| Structure Type | Than Pattern | Then Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Comparison | Adjective + than | Not used |
| With More | More + adjective + than | Not used |
| Sequence | Not used | Clause + then + clause |
| Time Reference | Not used | Back then |
| Command | Not used | Verb + , then + verb |
If the word follows a comparative adjective, it must be Than. If the word shows what happens next or refers to time, it must be Then.
When to Use Than and When to Use Then
Choosing between Than vs Then becomes simple when you check whether the sentence compares two things or shows sequence.
Use Than when the sentence refers to:
- Comparison between two people or things
- Comparative adjectives
- Words like more, less, better, rather
Examples:
- She is taller than her brother.
- This car is faster than that one.
- He works harder than before.
- I prefer coffee than tea.
- This test is easier than the last one.
- She is more confident than last year.
- The weather is warmer than yesterday.
- He arrived earlier than expected.
- This route is shorter than the other.
- I would rather stay home than go out.
Use Then when the sentence refers to:
- Time
- Order of events
- Sequence
- Result
Examples:
- Finish your homework, then relax.
- She called me, and then she left.
- Back then, life was different.
- Press the button, then wait.
- He apologized, and then he smiled.
- We will eat dinner, then watch a movie.
- Save the file, then close the program.
- She paused, then continued speaking.
- First read, then write.
- Since then, everything changed.
If the word connects a comparison, choose Than. If it shows what happens next or refers to time, choose Then.
Context Based Usage Guide
Context provides strong clues in Than vs Then decisions.
Than frequently appears:
- After comparative adjectives
- After more or less
- In preference structures
- With rather
Examples:
- Better than
- More interesting than
- Less expensive than
- Rather than
Then frequently appears:
- After commas
- At the beginning of a clause
- In time references
- In instructions
Examples:
- And then
- Back then
- By then
- First this, then that
You may notice a helpful clue. If the sentence contains a comparative word like better or more, the correct choice is usually Than.
Grammar Difference Between Than and Then
The grammar difference between Than vs Then is structural.
Than is a conjunction used in comparisons.
Then is an adverb used for time or sequence.
Than connects two elements being compared:
- She is taller than me.
- This book is better than that one.
Then modifies verbs or clauses to show order:
- She finished school and then got a job.
- We ate dinner and then watched a movie.
If the sentence compares two things, use Than. If it describes time or sequence, use Then.
Pronunciation Difference Between Than and Then
Although Than vs Then look similar, their pronunciation has a slight vowel difference. In natural speech, the contrast can sound subtle, which is why confusion often appears in writing.
Than usually has a short “a” sound, like in the word cat.
Then usually has a short “e” sound, like in the word pen.
Below is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Than | Then |
|---|---|---|
| Part of Speech | Conjunction | Adverb |
| Vowel Sound | Short “a” | Short “e” |
| Main Use | Comparison | Time or sequence |
| Common Pairing | Better than | And then |
Say them slowly:
Than
Then
Even though the vowel sound differs, fast speech can blur the distinction. Therefore, sentence structure is more reliable than sound when deciding which word to use.
Common Mistakes With Than and Then
Most mistakes in Than vs Then happen when writers focus on sound instead of grammar. Since the words are close in pronunciation, the wrong spelling is often typed.
Below are frequent mistakes with corrections.
- Incorrect: She is taller then me.
Correct: She is taller than me. - Incorrect: I would rather stay home then go out.
Correct: I would rather stay home than go out. - Incorrect: This test is easier then the last one.
Correct: This test is easier than the last one. - Incorrect: Finish your homework, than relax.
Correct: Finish your homework, then relax. - Incorrect: He called me and than left.
Correct: He called me and then left. - Incorrect: Back than, life was different.
Correct: Back then, life was different. - Incorrect: More better then before.
Correct: Better than before. - Incorrect: First read, than write.
Correct: First read, then write. - Incorrect: She arrived earlier then expected.
Correct: She arrived earlier than expected. - Incorrect: Save the file than close it.
Correct: Save the file, then close it.
Notice the consistent pattern. If the sentence compares two things, use Than. If it shows order or time, use Then.
FAQs
The main difference in Than vs Then is function. Than is used for comparison between two things. Then refers to time, sequence, or what happens next.
Use Than after comparative words such as better, more, less, taller, or rather. If the sentence compares two people, objects, or ideas, Than is correct.
Use Then when referring to time or sequence. It often appears in instructions or storytelling, such as Finish your work, then relax.
No. Then cannot replace Than in comparisons. For example, She is taller than me is correct. Using Then would make the sentence incorrect.
If the sentence includes comparison, choose Than. If it refers to time or what happens next, choose Then. Checking the sentence structure helps avoid confusion.
Final Summary
Than vs Then may look and sound similar, but their meanings are completely different. Than is a conjunction used for comparison. Then is an adverb used to show time, order, or result. If the sentence compares two things, choose Than. If it describes what happens next or refers to time, choose Then. Understanding this distinction prevents common spelling errors and strengthens sentence accuracy.
Read More

