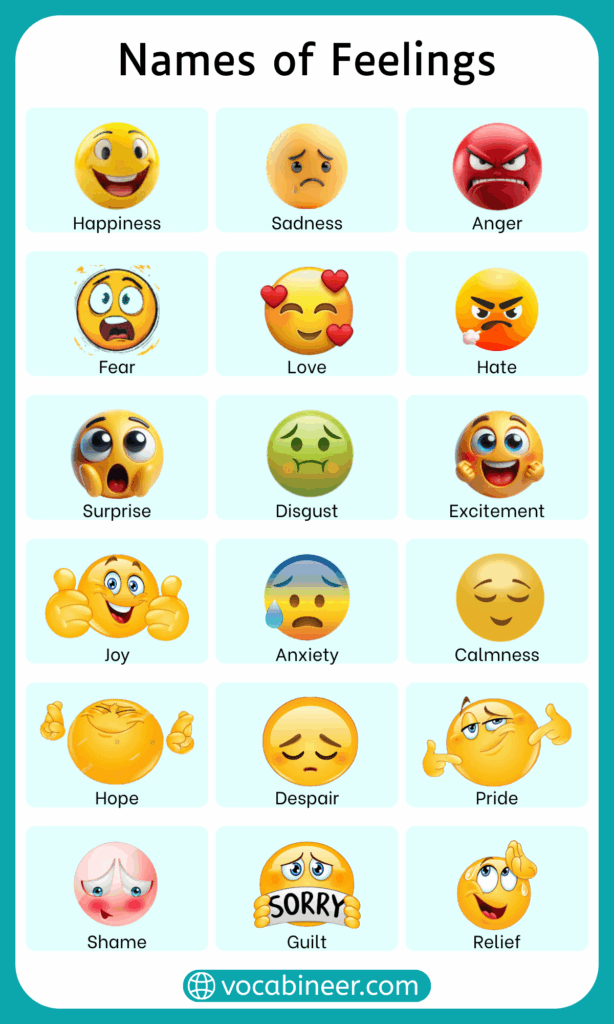
Feelings and emotions are natural human reactions that shape how we think, speak, and act in daily life. Each one carries a specific name, making it easier to describe different experiences in simple and clear ways. In this article, you will explore types of feelings and emotions and their names. Learning them supports better communication in conversations, helps with school projects, and adds meaning to creative tasks and personal expression.
In This Page
Basic Types of Feelings and Emotions in English
Feelings and emotions describe how people react to situations, thoughts, and experiences in daily life. These emotional states influence facial expressions, tone of voice, body movement, and behavior. Learning the basic types of feelings and emotions helps readers recognize emotional signals, understand reactions, and describe personal experiences clearly in everyday communication.
- Happiness: A positive emotional state showing joy, pleasure, comfort, and emotional satisfaction
- Sadness: An emotional response reflecting loss, disappointment, grief, or emotional heaviness
- Anger: A strong emotional reaction showing frustration, irritation, or displeasure
- Fear: An emotional response to danger, uncertainty, or threat, often linked to nervousness or anxiety
- Surprise: A sudden emotional reaction to unexpected events, showing shock or amazement
- Disgust: A feeling of strong dislike or discomfort toward something unpleasant
- Excitement: A high-energy emotional state showing enthusiasm, joy, or eager anticipation
- Nervousness: A feeling of worry or tension before uncertain situations
- Confusion: An emotional state showing lack of understanding or mental uncertainty
- Pride: A positive emotion reflecting achievement, confidence, or satisfaction
- Embarrassment: A feeling of discomfort or self-consciousness in social situations
- Calmness: A peaceful emotional state showing relaxation and emotional balance
- Shame: A painful feeling caused by guilt, mistake, or social discomfort
- Relief: A relaxed feeling after stress, worry, or difficulty ends
- Curiosity: A feeling of interest and desire to learn or understand something new
- Frustration: An emotional reaction caused by repeated difficulty or blocked effort
- Hope: A positive emotional state showing expectation and belief in good outcomes
- Love: A deep emotional connection showing care, affection, and emotional warmth
Extended Human Emotions
Beyond the six basics, humans experience a wide range of extended emotions. These add depth to our lives and help us describe relationships, ambitions, and more subtle experiences.
- Love: A strong connection felt toward family, friends, or partners.
- Trust: Confidence in someone’s honesty, such as depending on a teacher.
- Anticipation: Excitement or anxiety about the future, like waiting for exam results.
- Pride: Satisfaction from success, such as scoring high marks.
- Shame: A painful feeling caused by failure or mistakes.
- Guilt: Regret over a wrong action, like telling a lie.
- Jealousy: Feeling upset when others have what we want.
- Calmness: A peaceful state, like sitting in nature.
- Excitement: Energy and joy when something enjoyable is about to happen.
Positive and Negative Emotions Explained
Emotions can be grouped into two broad types. Positive ones give energy, comfort, and motivation. Negative ones may feel heavy but often protect us, signal problems, or encourage change.
Positive Emotions
- Happiness: Brings joy, laughter, and comfort in daily life.
- Love: Builds strong bonds with family, friends, or partners.
- Gratitude: Encourages kindness and appreciation for what we have.
- Hope: Provides strength to look forward with confidence.
- Pride: Creates satisfaction after effort or success.
Negative Emotions
- Anger: A strong reaction to unfairness or harm.
- Fear: Alerts us to possible danger or risk.
- Sadness: Helps us process loss or disappointment.
- Guilt: Signals regret when we have done wrong.
- Jealousy: Brings tension when comparing ourselves with others.
Complex Types of Feelings for Someone
Relationships create complex emotions that may mix both positive and negative tones. These feelings help us connect deeply or express when ties with others bring joy or conflict.
- Affection: Warmth and closeness toward someone.
- Admiration: Respect for someone’s qualities or talents.
- Attraction: A strong pull toward a person.
- Resentment: Lingering anger when treated unfairly.
- Compassion: Caring concern for another’s suffering.
Physical Connection Between Feelings and the Body
Emotions are not only in the mind. They often affect how the body feels, moves, or reacts in everyday situations. These physical signs help us recognize what we are experiencing.
- Fear: Quick heartbeat, sweaty palms, and shaky hands prepare the body to escape danger.
- Happiness: Relaxed muscles and warm energy create a sense of comfort.
- Anger: A red face, tense jaw, or clenched fists signal frustration or conflict.
- Sadness: Tears, drooping posture, and low energy often follow disappointment or loss.
- Excitement: Extra energy, faster breathing, and smiles reflect anticipation of something enjoyable.
Types of Feelings and Emotions in Daily Life
Our emotions appear in daily settings, shaping how we act and respond. From family to work, they help us interact, solve problems, and express what matters most to us.
- Family: Love, care, pride, and sometimes frustration.
- School: Excitement, stress, or satisfaction with learning.
- Work: Motivation, anxiety, or accomplishment.
- Relationships: Affection, trust, or conflict.
FAQs on Types of Feelings and Emotions
The six universal emotions are happiness, sadness, anger, fear, disgust, and surprise, which are recognized across all cultures.
Primary emotions are basic reactions like joy or fear. Secondary emotions, such as frustration or pride, come from a mix of those primary feelings.
Some theories list six, others list eight, and newer research expands the range to more than twenty distinct emotion categories.
Emotions are quick, automatic responses to events. Feelings are how we consciously experience and describe those emotional responses.
This phrase usually means having mixed or unclear emotions. It’s often used when someone cannot easily name what they feel.
Read More